Cognition and memory
Understanding how animal models learn, remember, and adapt is crucial in advancing our knowledge of neurodegenarative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. However, there is not just one test for one type of cognition. For example:
- Spatial Memory
- Recognition
- Associative learning
- Operant conditioning
- Reversal learning

What is Cognition and Memory?
Cognition and memory are essential for understanding animal behavior, reflecting how animals process and retain information. In research, these processes are studied though various tests that reflect the varying parts of memory and cognition. These measures help researchers evaluate brain function and the impact of interventions, particularly in models of neurological and psychological disorders.
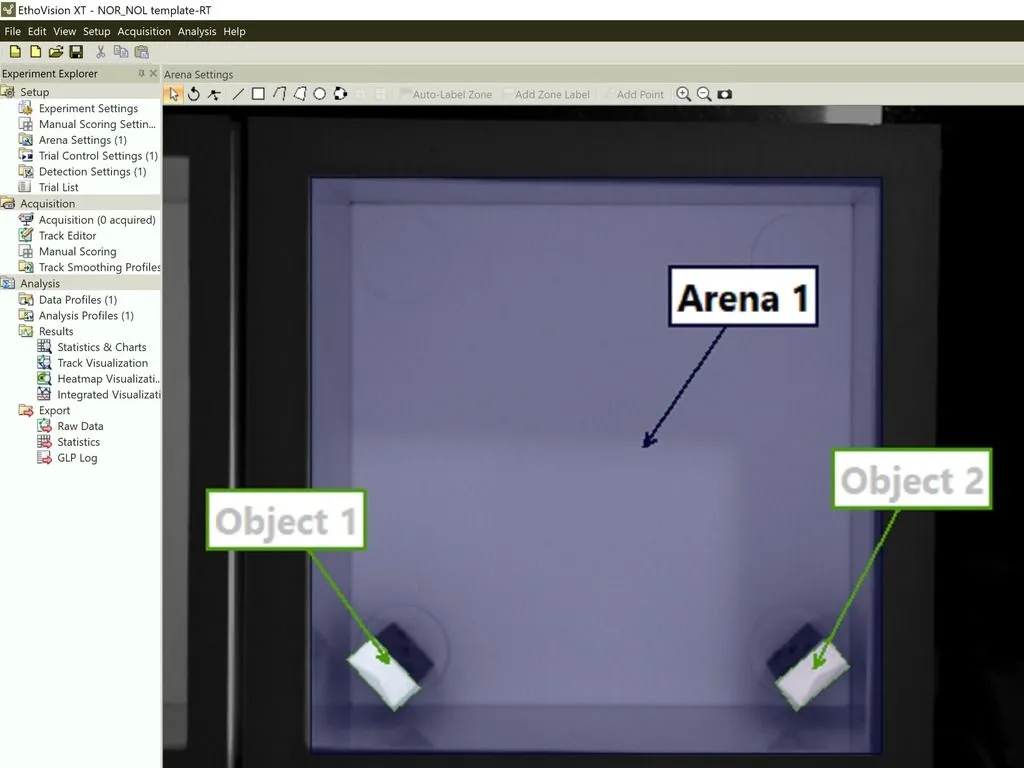
Short and long-term memory
Short-term memory enables animals to quickly process and respond to new information, crucial for navigating environments, pursuing goals, and enhancing survival. Long-term memory stores essential information over time, from territory layouts to experiences linked to rewards or dangers.
- Working memory is a short-term memory used to retain and manipulate information during a task, often assessed in animals by their ability to remember objects, stimuli, or locations within a single session.
- Episodic memory is a type of long-term memory involving specific events tied to particular times and places, often assessed in animals through location-based tasks.
Considering the effect of interventions on both short and long-term memory is important for accessing the full behavioral response. Both types of memory access different parts of the brain, and therefore can be impacted differently by certain disorders.
Associative learning Tests
Associative learning is a process in which a new response becomes associated with a particular stimulus. Like, Pavlovian learning is a form of associative learning, since this is typically induced in subjects that associate stimuli with a negative (aversive) stimulus or situation. Associative learning works in three broad steps:
- Induce a stimulus (typically negative, but can be neutral or positive).
- Learn to connect the stimuli to a response.
- Reinforce this response and therefore strengthen the behavioral pattern.
The ability to associate stimuli with specific behaviors is a key indicator of an animal's cognitive abilities. Animals experiencing cognitive decline due to psychological or neurological conditions tend to perform worse on these tests, making it possible to assess the effectiveness of treatments by measuring improvements in their performance.

Reversal learning
Cognitive flexibility is the ability to rapidly adapt behavior while facing specific circumstances. Essentially, it measures an animal's cognitive flexibility: the capacity to unlearn a previously learned behavior.
- Cognitive flexibilty is essential in the development of behavior, enabling an animal to modify its behavior to changes in the environment.
- How quickly and succesfully an animal adepts its behavior is a great indicator of brain function.
Measuring reversal learning in animals is a validated method for measuring the impact of symptoms and treatment of various brain disorders. These tests provide insights into the adaptability of cognitive function in your models.
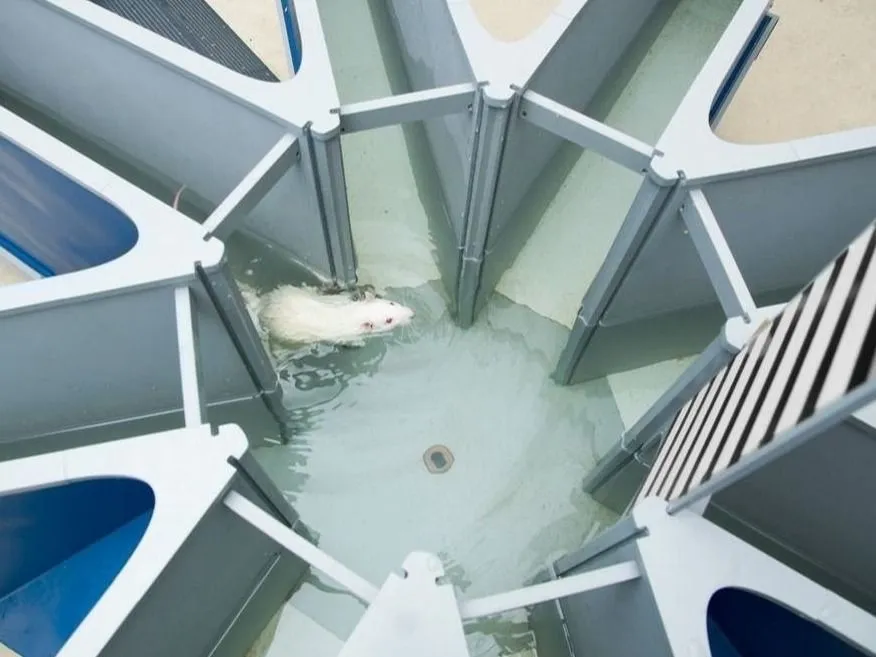

Spatial memory
Spatial memory concerns the association of an organism in a three-dimensional environment. In other words: an animal learning its position in a given space. This learning relies on visual, but also acoustic and olfactory cues.
- Allocentric memory: Encodes the location of an object based on its relationship to other objects in the environment, independent of your position.
- Egocentric memory: Encodes the location of objects relative to your own current position or viewpoint.
Measuring spatial memory in rodents or zebrafish is essential for studying the impact certain interventions have on the brain. This gives animal models great translational value when studying diseases like Alzheimer's disease, TBI and Schizophrenia.
Explore cognition with a free e-book
Basic behavioral neuroscience in rodents
Want some more literature on the basic (behavioral) neuroscience in rodents? Download our free e-book. In this e-book you can, among other things, read about the basics of what learning and memory testing in rodents is and how to execute the most common protocols.
How to measure Cognition and memory
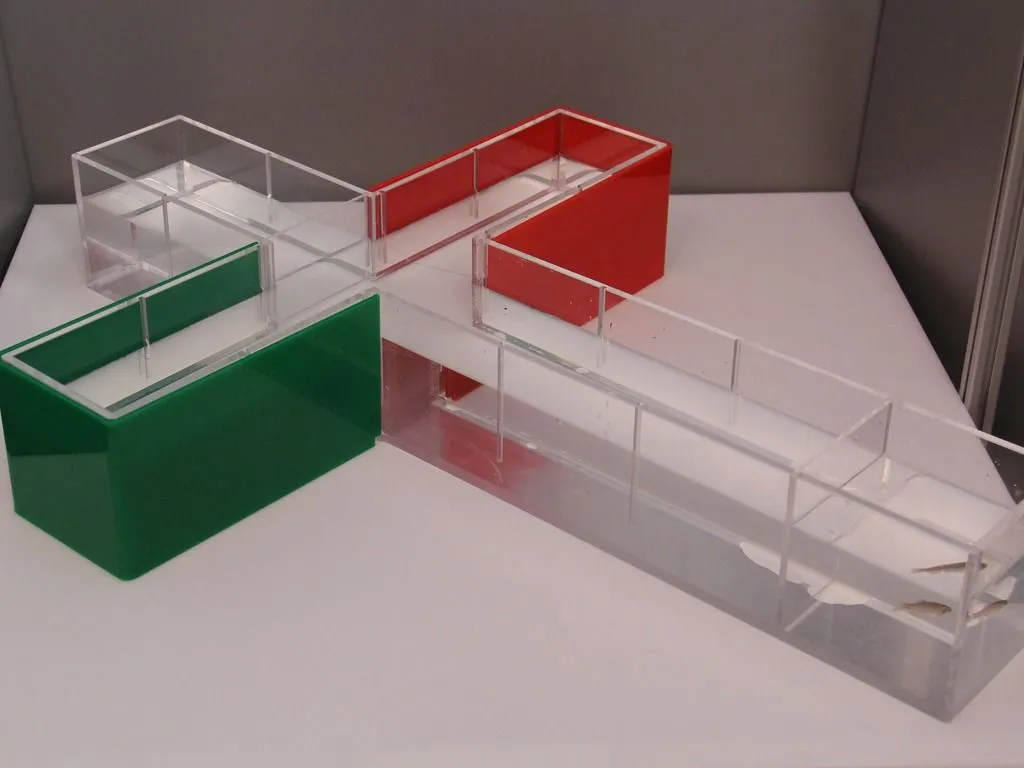
Y/T-maze
The Y/T maze (or cross maze in zebrafish) is used to
test the learning and memory of animal models. It is often used to test reversal
learning, learning retention, and preference testing.
The time spend in certain arms of
the maze can be tracked by EthoVision XT. This ensures that data is corrected easily and
accurately.
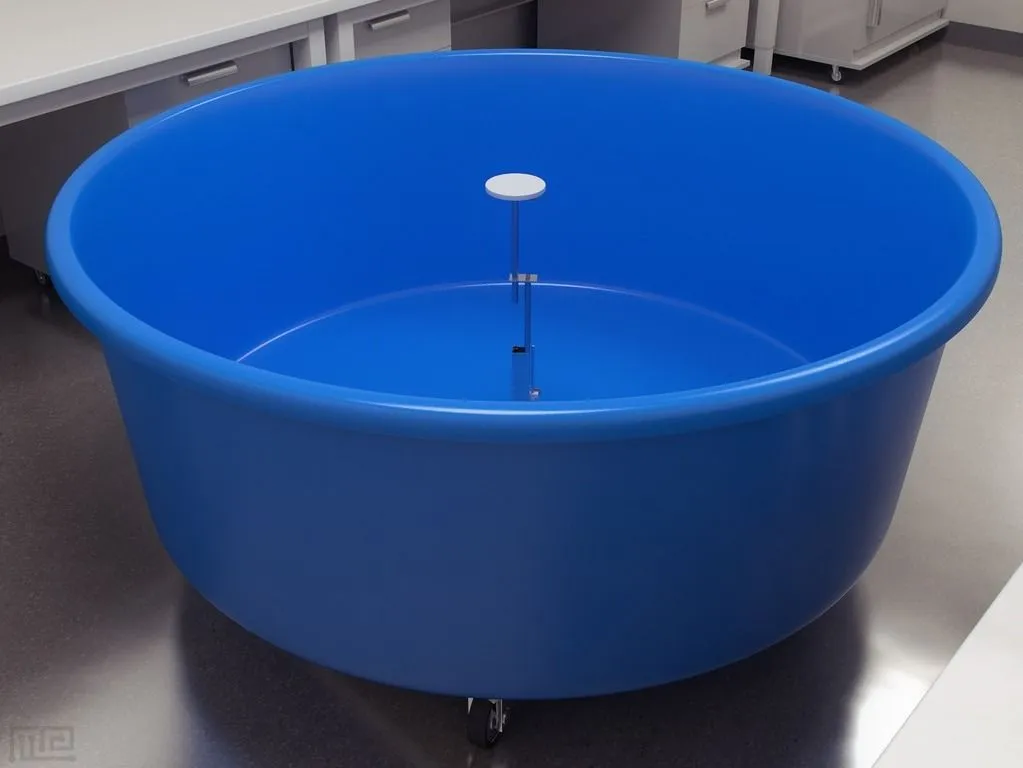

Morris water maze
The Morris water maze is a well-validated test for
spatial learning. At Noldus, we offer not only high quality mazes in various sizes and
colors but also the best tracking system available.
EthoVision XT is essential for
measuring the average distance to the platform and swimming patterns. This is important
for trials where the platform is moved or removed.

Novel object test
the novel object test assesses cognitive function and
exploratory behavior in rodents by gauging their response to a new object.
With
EthoVision XT, you can precisely track the distance of the nose-point of the animal to
the novel object. Proper hardware and software ensure that your data is consistent and reliable.
Cincinnati maze
The Cincinnati maze is used to test egocentric
navigation, learning and memory in rodents. An animal swims throught he maze trying to find the exit platform.
With EthoVision XT you can easily measure
the distance moved, number of errors, and time spend reaching the goal.

Barnes maze
The goal of a Barnes maze is to study spatial learning
and memory. The rodent is supposed to find the box that is positioned beneath one of the
holes. The mouse or rat uses visual aids outside of the arena to find a food reward.
EthoVision XT allows you to easily track which holes the animal is investigating and how
long it takes for it to find the reward.
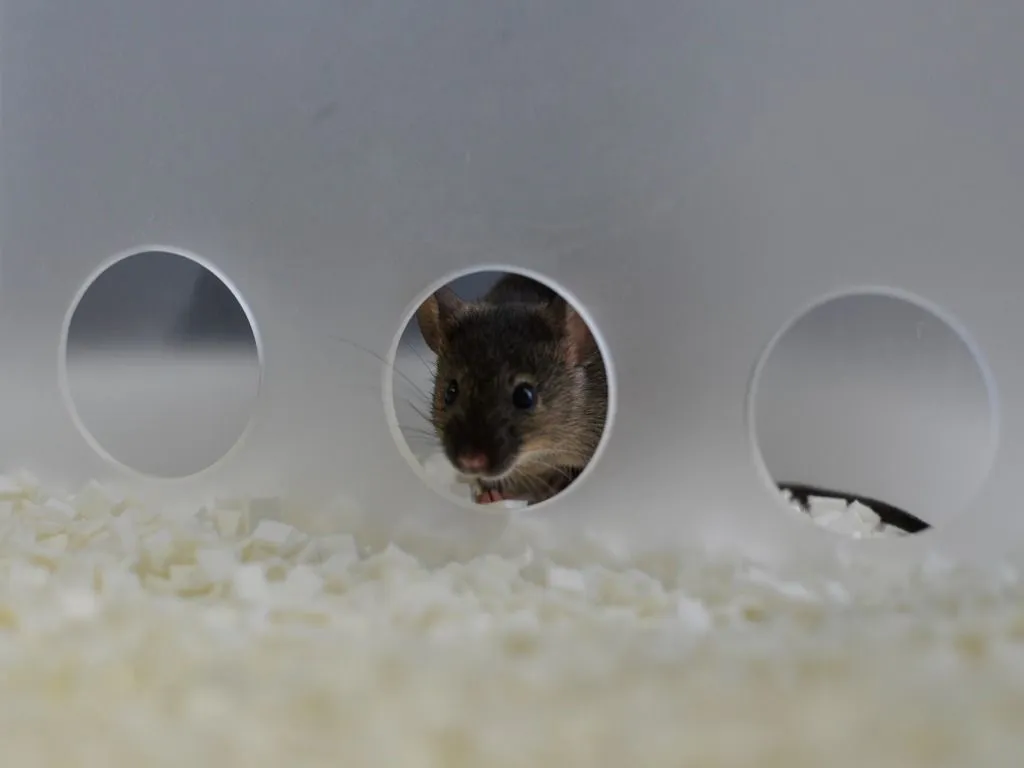

CognitionWall
The CognitionWall by Sylics is an wall containing three
entrances placed in front of a reward dispenser. Once the animal has learned which
entrance activates the reward dispenser the correct answers can be changed to assess the
animal's cognitive flexibility.
CognitionWall can easily be fitted in PhenoTyper instrumented home cage.
Featured blog posts
Using video tracking to study operant behavior in rodents
Scientists from Idorsia Pharmaceuticals in Switzerland provide an expert view on operant behavior, and how we can improve our understanding of this complex behavior with the help of video tracking.
Unlocking the link between CNS infections and cognitive decline
Bacterial infections in the brain can have lasting effects even after recovery. In this blog we will look a study that used PhenoTyper and the CognitionWall to study the mechanisms behind this cognitive impairment.
Advancing the novel object test: 3D printing and deep learning
To improve standardisation and consistency in the novel object test, Spry et al designed the 'CapTouch' system: capacative objects that can automatically register interaction. But what about deep learning in EthoVision XT?
Are you looking for advice on your application?
Do you want to learn more about how to apply Noldus products to your
research, or do you need advice from our team of behavioral experts?
Noldus is here to assist you throughout the whole process.