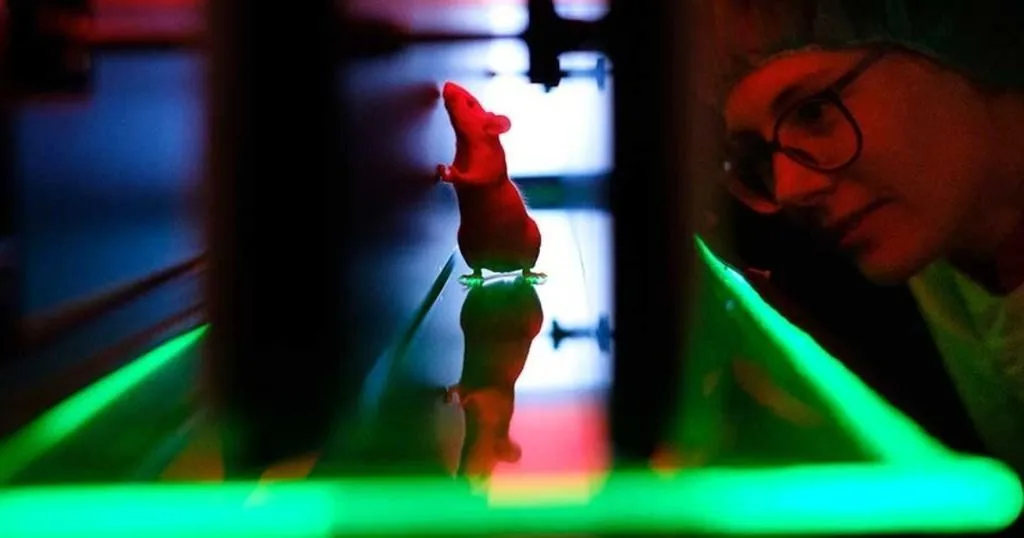
Parkinson’s & gait impairment: comparing rats and humans
Gait impairment is one of the most prominent symptoms of Parkinson's disease. For good research you need good models and good tests.
Posted by
Published on
Thu 05 Feb. 2015
Topics
| CatWalk XT | Gait | Locomotion | Parkinson's Disease |
When you hear about Parkinson’s disease (PD), the first thing that comes to mind is probably impaired movement. And that there is no cure. As PD is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases, you can imagine why it is the focus of many drug development and clinical studies.
Studying gait impairment of PD
Dr. Ming Zhou and colleagues (Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China) felt that gait impairment, though it is one of the most prominent symptoms of PD, is still insufficiently studied in research. Before learning how to treat any symptoms, however, you first need to be able to examine them in detail. Simply put, you’ll need two basic ingredients; good models and good tests.
Parkinsonism in rats
PD – its symptoms, neurology, and possible treatments – is often studied in rat models. Dr. Zhou et al. first created different rat models for PD and compared their locomotion to clinical symptoms in human patients. A common method to induce Parkinsonism in rats is by injecting oxidopamine into the brain, thus destroying dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons. In this particular study, three different injection sites were used (the caudate putamen (CPU), medial forebrain bundle (MFB) and substantia nigra compact (SNC)) to create three different models.
How to effectively study gait impairment
To evaluate the gait of their rats, Zhou and colleagues used CatWalk XT, a gait assessment apparatus that automatically records the footprints of a rat moving voluntarily (completely unforced) from one end of a walkway to the other. Using the footprint data (their placement, dimensions, timing, etc.), the software measured and calculated several parameters.
And the best model is…
The researchers found that the MFB model was the best out of the three for studying PD related gait impairment, showing a stable loss of dopaminergic neurons as well as accompanying gait impairments.
Comparing rats and humans
Stance, step cycle, and duty cycle were all increased in the impaired rats, similar to clinical PD symptoms of taking small, slow steps. There also was a longer duration of contact between the paws and the glass, which can be compared to PD patients having an increased stance duration. Additionally, the increase of the terminal dual stance in limbs that was found in this study can be translated to the delays or freezing of gait, or gait hesitation, as seen in these patients. These results may be useful in future research into the disease progression and therapeutic methods for PD.
Reference
Zhou, M.; Zhang, W.; Chang, J.; Wang, J.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Y.; Wen, P.; Xiao, H. (2015). Gait analysis in three different 6-hydroxydopamine rat models of Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience Letters, 584, 184-189.
Related Posts

What gait can tell: 3 blogs that will help you understand

Time based relations in gait analysis

