Understanding adolescent emotions
How are adolescents’ emotions socialized by mothers and close friends? A recent study focuses on dealing with depression in adolescence.
Posted by
Published on
Tue 12 Apr. 2016

I was waiting for my exam results, and so was the son of our neighbors. And then there was a bang. A really loud one. I could guess the outcome of his exam simply by hearing that bang.
Afterwards we indeed heard that he didn’t pass his exam and that the telephone suffered the consequences… Emotions are hard to deal with. I would have felt the same if I had to retake exams. When you are young and experience so many challenges, it is hard to deal with emotions.
During my adolescence, there were computer games wanting to be played, friends wanting to go out with, and TV programs wanting to be watched…which resulted in schoolwork receiving a little less attention.
Dealing with depression
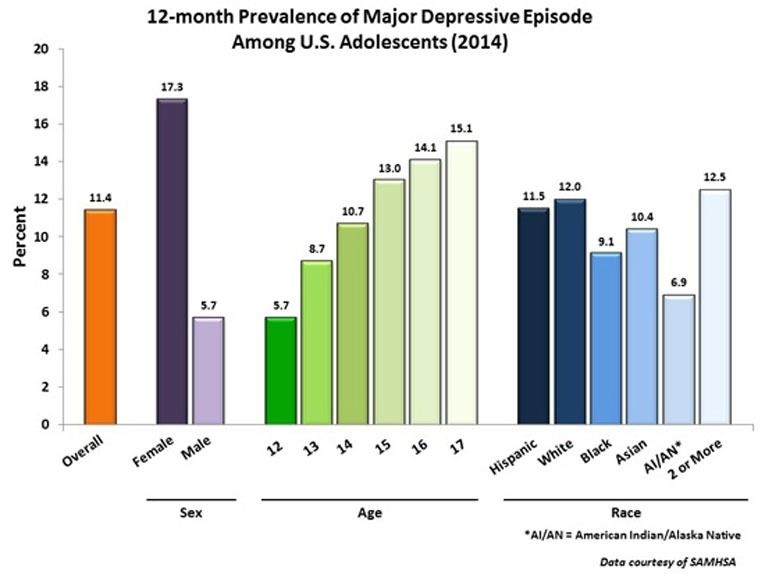
A few days ago, I read a report about adolescent emotions from the NIMH (Bethesda, MD). It stated that in 2014, 11% of the 12 to 17 year-olds in the US reported at least one major depressive episode over the period of a year [1].
That’s almost 3 million adolescents!
Jessica Lougheed from Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, and colleagues explain that depression is considered a disorder of emotion regulation, as it is associated with difficulties in regulating both positive and negative emotions.
Regulate your own emotions
In adolescence, the ability to regulate emotions is heavily challenged by numerous biological, social, and psychological changes. By learning to adequately regulate emotions, people are attempting to control the intensity, form, and duration of the emotion [2].
Adolescents should learn to increase or decrease the intensity of the moment. I now see that it’s this mechanism making emotions stronger.
Observing interactions
Jessica Lougheed and colleagues set up a study in order to understand how adolescents’ emotions are socialized by their mothers and close friends, since both mothers and close friends play important roles in adolescent lives.
In total they observed 83 adolescents. They recorded interactions on video and coded interactions using The Observer XT professional analysis software.
Understanding adolescent emotions
The sessions were conducted either in participants’ homes or in a private location at their school. The task given by the researchers was an interaction task consisting of two 7 minute conflict discussions. Prior to the interaction task, the participants acclimatized to the video camera in a ‘warm-up’ discussion about how to plan a party.
According to Lougheed’s study, this work is the first step towards understanding the microsocial processes in both maternal and peer relationships that can factor into regulating adolescent depressive symptoms.
Depressive symptoms under investigation
The researchers found that mothers were less likely to show supportiveness to adolescents with higher depressive symptoms, regardless of adolescents’ expressed emotions. Peers were less likely to up-regulate adolescent positive emotions for adolescents with higher depressive symptoms.
The researchers conclude that maternal and peer emotion socialization play a role in late-adolescent depressive symptoms, but in different ways.
There is a possible confound in the study: adolescents with depressive symptoms may also have mothers with depressive symptoms, Lougheed et al. note.
Future studies should include measurements of all interaction partners’ depressive symptoms (for example, mothers and peers in this study). Furthermore, Lougheed et al. indicate that an important direction for future research will be to incorporate both microsocial and longitudinal designs. They believe this will shed light on the specific social processes involved in the etiology of depression, as well as how specific features of depressive symptoms affect real-time social dynamics.
References
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/major-depression.shtml
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regulation_of_emotion
- Lougheed, J.P.; Craig, W.M.; Pepler, D.; Connolly, J.; O’Hara, A.; Granic, I.; Hollenstein, T. (2015). Maternal and peer regulation of adolescent emotion: associations with depressive symptoms. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, doi:10.1007/s10802-015-0084-x.
Related Posts

How emotions are made

FaceReader and different scientific theories on emotion

